October 31, 2025
AI improves epidemic forecasts
FIAS researchers combine disease models with artificial intelligence to better understand how diseases spread.
More accurate predictions of epidemics are important for combating infectious diseases and protecting public health. A research team at the Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies (FIAS) has developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) for this purpose. It combines classic models of disease spread with modern deep learning methods to better capture differences in the temporal and spatial progression of an epidemic.
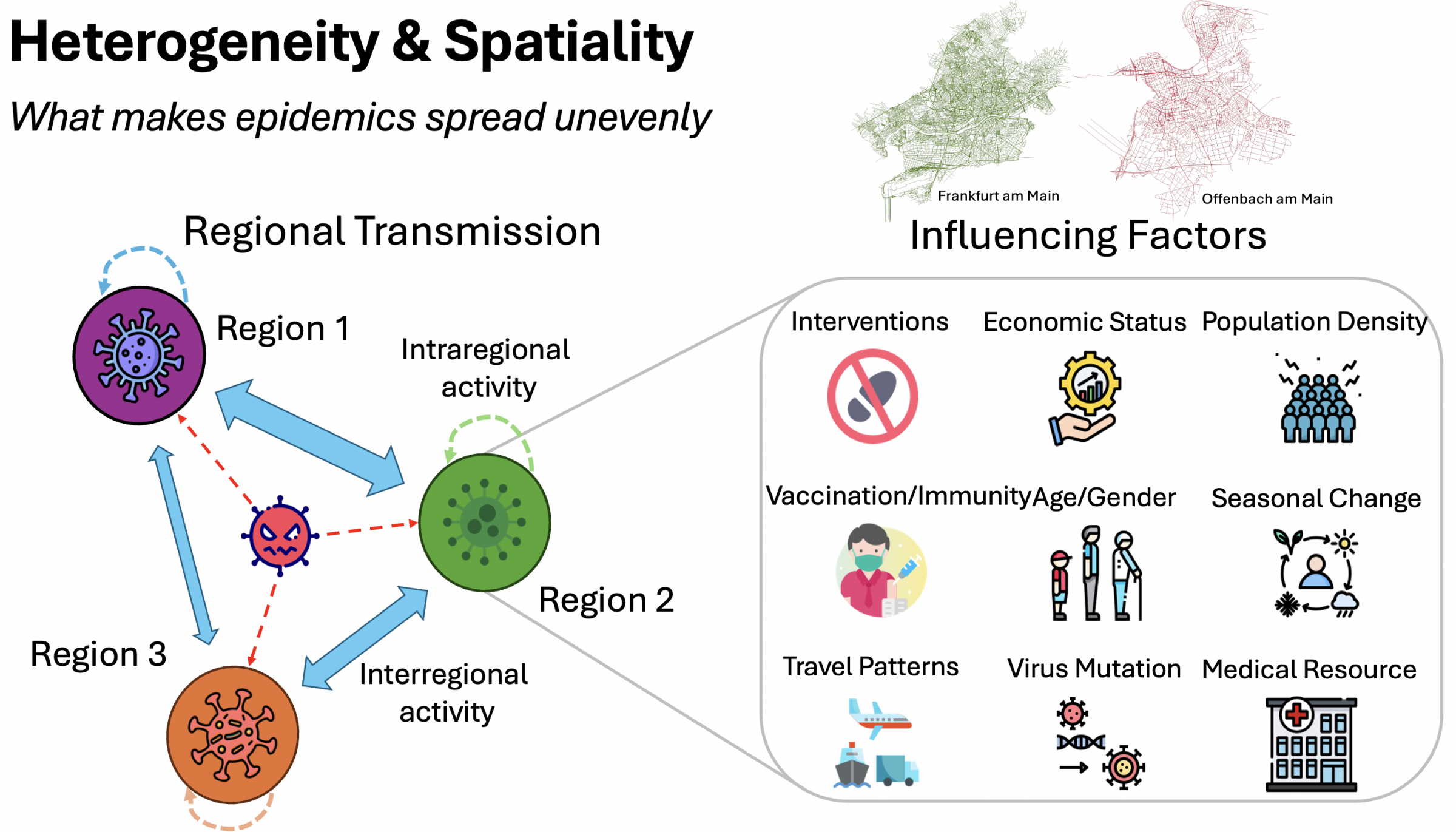
Doctoral student Shuai Han, Lukas Stelz, and supervising FIAS senior fellows Kai Zhou and Horst Stöcker, together with FIAS fellow Thomas Sokolowski, named their model Epidemiology-informed Spatiotemporal Graph Neural Network (EISTGNN). It shows how the disease spreads at different speeds in different regions and how contacts change over time.
Unlike conventional black-box AI models, EISTGNN learns directly from important epidemiological values such as infection and recovery rates and contacts between regions, enabling the model to explain the spread of the disease better and more comprehensibly. The model shows how different mobility patterns, political interventions, and social events influence transmission in different regions. Measured against large data sets from China and Germany, EISTGNN consistently outperforms current approaches while providing transparent insights into regional outbreak dynamics.
“Our model combines epidemiological approaches with the flexible power of artificial intelligence to deliver results that are both understandable and adaptable,” Han said. “Not only does it predict epidemic trends more accurately, it also explains why and how they occur.”
This study helps bridge the gap between mechanistic modeling and artificial intelligence, demonstrating how theoretical understanding and data-driven learning can work together to explain complex epidemic dynamics. Future work will extend this approach to related fields and real-world applications.
Publication:
Shuai Han, Lukas Stelz, Thomas R. Sokolowski, Kai Zhou, Horst Stöcker, Epidemiology-informed Spatiotemporal Graph Neural Network for heterogeneity-driven interpretable epidemic forecasting, Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 162 (2025) 112764. DOI: 10.1016/j.engappai.2025.112764